Quick Start Guide
Robot-Assisted Surgery (RAS) At Sunnybrook
-
Dr. Alia Busuttil is the Anesthesiology clinical lead for the RAS program, debuted in October 2024.
-
The da Vinci Xi robotic surgical platform is located in OR 2.
-
Surgical services include urology, gynecology, general surgery and ENT.
Benefits Of Robot-Assisted Surgery
-
Magnified three-dimensional vision.
-
Digitally controlled hand movement with algorithm to filter out natural hands tremor.
-
Higher degree of maneuverability / superior dexterity of robotic instruments.
-
Reduction in blood loss, length of stay, 30-day overall complication rate and post op pain compared to open procedures. When compared with MIS, there is still some evidence to suggest reduced length of stay, conversion rate and EBL.
-
There is also evidence to supports improved resection negative margin in cancer cases.
Disadvantages Of Robot-Assisted Surgery
-
Capital cost.
-
Steep learning curve.
-
Longer procedure time.
-
Potential complications related to prolonged extreme position (e.g. steep Trendelenburg) and pneumoperitoneum for prolonged period of time (see anesthesia considerations below).
Anesthesia Considerations
-
Both arms tucked and there will be limited access of patient during surgery. Important to secure all lines and ETT to avoid any kink. Ensure IV access is readily accessible.
-
Prolonged surgical duration necessitates meticulous positioning and padding to avoid pressure injury, neuropraxia and compartment syndrome. TE prophylaxis with systemic anticoagulant +/- pneumatic stockings.
-
Prolonged extreme position e.g. steep Trendelenburg (20-30 degrees) can lead to increased intraocular pressure, intracranial pressure and airway edema. Patients with severe / untreated glaucoma, history of intracranial SOL are relatively contraindicated for RAS. Also be mindful about airway edema, prudent to perform leak test before extubation. Restrictive fluid management where possible to minimize edema.
-
Protective mat placed under patient to minimize slipping and provide padding.
-
Potential for endobronchial migration of ETT upon steep Trendelenburg.
-
Chemosis / conjunctival edema after prolonged trendelenburg, hence important to meticulously tape eyelids. Other forms of occlusive eyelid dressings / foam goggles and gentle application of Lacrilube is recommended. RAS in steep Trendelenburg causes 3-5 folds increase in corneal abrasion. Keep in mind also other remote possibility of rare ocular complication such ischemic optic neuropathy.
-
Prolonged CO2 pneumoperitoneum - reduction in FRC & lungs compliance, further exacerbated by trendelenburg position. Ventilation strategy: PCV, lungs protection VT 6-8ml/kg ideal body weight, PEEP 4-8 cm H2O, I:E ratio of 2:1 or 1:1 has be shown to improve CO2 clearance. To optimize oxygenation, recruitment manoeuvre can be used to decrease atelectasis, improve alveolar ventilation and decrease intrapulmonary shunting but be mindful about reduction in venous return and hypotension.
-
Possibility of venous air embolism and subcutaneous emphysema.
-
Cardiovascular effect of pneumoperitoneum - increase in CVP, PAP with a compensatory drop in HR; compression of aorta leads to increase in SVR that results in reduction of stroke volume and CO & increase in myocardial oxygen demand.
-
Consider NG tube to reduce gravity-induced passive regurgitation in Trendelenburg position.
-
Deep muscle paralysis to avoid inadvertent patient movement and improve ventilation mechanics. Quantitative TOF neuromuscular monitoring would be beneficial.
-
MMA for optimal post op pain management, can consider truncal blocks e.g. TAP block.
Brief Overview Of da Vinci Xi
-
Intuitive Surgical Inc.'s 4th generation robotic platform.
-
The platform has been in production since 2014.
-
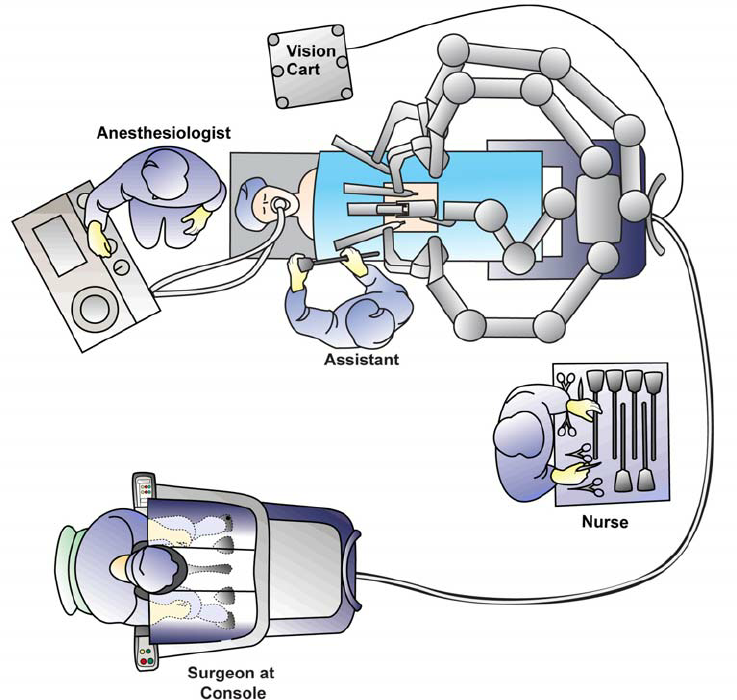
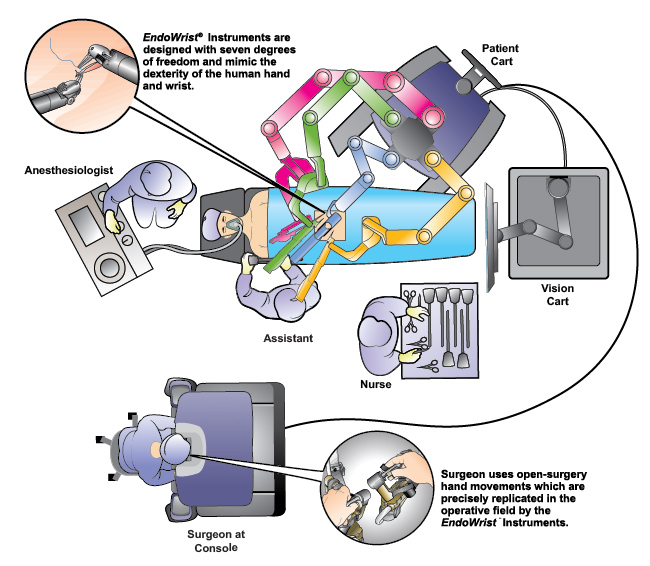
The system comprises of Three main components:
1. Surgeon Console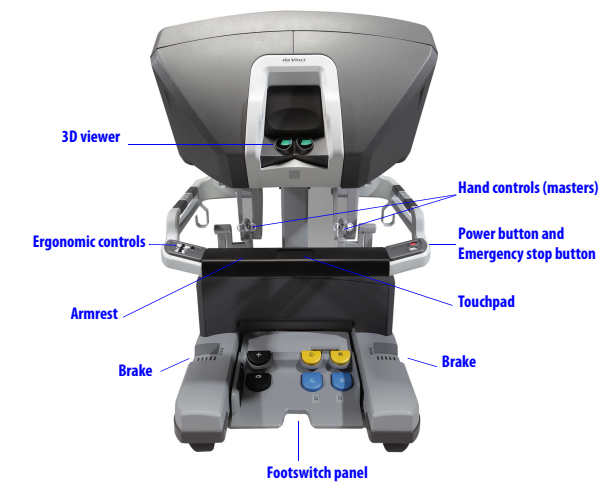
The operating surgeon seated at the Surgeon Console with three-dimensional endoscopic view of the surgical field and hand controls for instruments and endoscope.
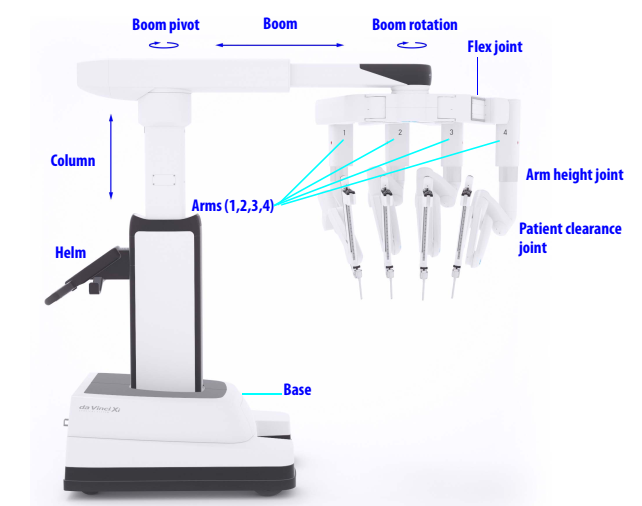
2. Patient Cart
Patient Cart Helm
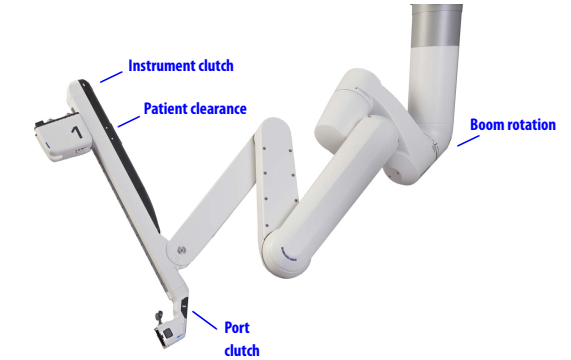
The draped patient cart is positioned by the OR table in the sterile field, exact cart orientation depends on each specific surgery, target anatomy and patient's position. Endoscope and instruments are attached / detached to each of the 4 arms by patient-side surgical assistant.
Close-up view of 1 of the 4 arms
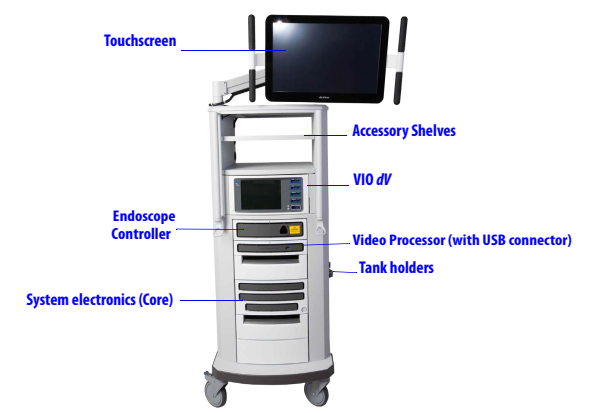
3. Vision Cart
The Vision Cart includes the supporting electronic equipment such as the light source and video image processing equipment for the endoscope and the main electronic and software processing units. The Vision Cart also has a touchscreen to view the endoscopic image and adjust system settings.
OR Configuration & Carts Placement
-
Surgeon Console is located outside the sterile field, positioned in such a way that the surgeon has an unobstructed view of the operative field, vision cart and be able to communicate directly with the rest of the OR team e.g. anesthesiologist, assistant surgeon and scrub nurse.
-
Patient Cart is properly draped and located within the sterile field. Its position is surgery-specific and dependant on surgeon's preference.
-
Vision Cart is positioned adjacent to the Patient Cart just outside the sterile field allowing assistant surgeon & scrub nurse to see the endoscopic surgical view.
-
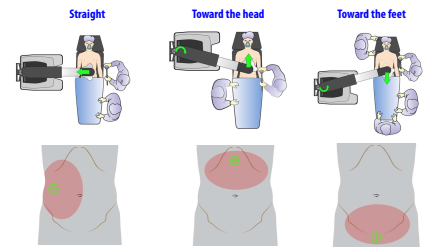
Surgeries of pelvic organs (e.g. prostatectomy), the Patient Cart can also be positioned between patient's legs.
-
Patient Cart position with respect to location of target anatomy.
Docking Of Patient Cart
-
Docking refers to the process of attaching Patient Cart instrument and camera arms to the patient.
-
Following are the sequential steps leading up to docking:
-
Anesthesia induction and intubation on the OR table.
-
Placement of additional IV / arterial lines / NG / Foley catheters.
-
Position the patient and OR table including necessary tilt.
-
Patient prepped and preliminary laparoscopy performed to assess intra-abdominal anatomy, suitability for robotic surgery and plan for locations of additional ports.
-
Additional ports (assistant / robotic instruments / camera) insertion.
-
Bring Patient Cart to the desirable final position.
-
Dock the camera arm first and then the instrument arms.
-
Once the arms are docked to the ports and instruments placed, patient position should not be changed. Any inadvertent patient's movement could potentially cause disastrous intra-abdominal trauma by the instruments / camera.
Emergency Undocking - unexpected complication e.g. bleeding or intraoperative cardiac arrest that necessitate undocking of the robot to facilitate resuscitation and / or conversion to open procedure. A well-defined and rehearsed undocking plan / protocol outlining steps of instrument withdrawal should be in place.
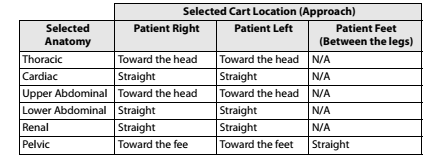
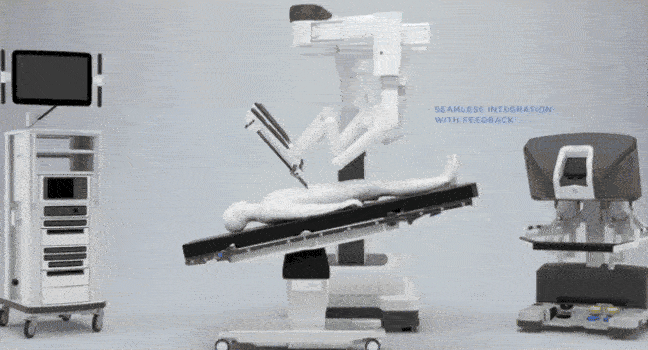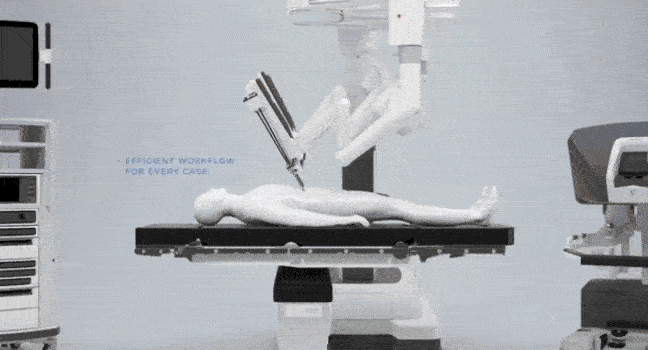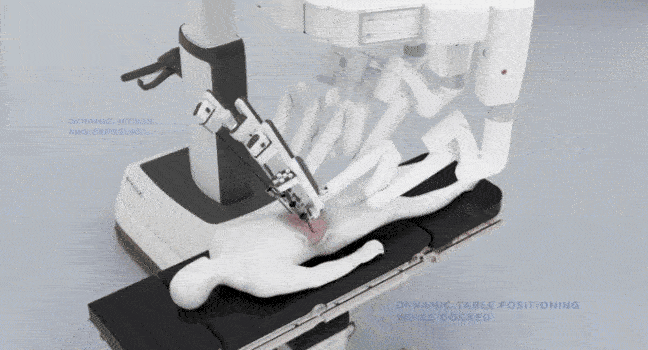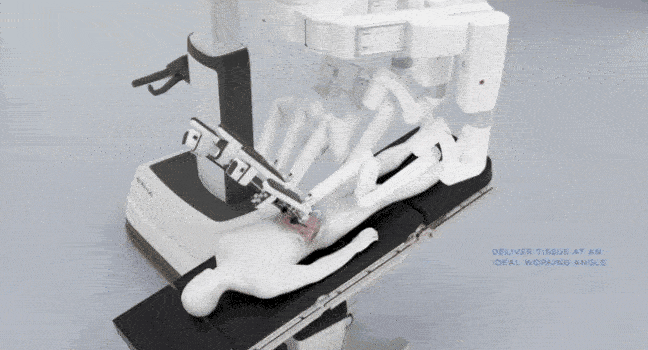
The specialized OR table (Baxter Hillrom TS7000dv) wirelessly pairs / communicates with the da Vinci Xi system to allow Integrated Table Motion (ITM) i.e. movement of the OR table is automatically coordinated with the robot so that the patient and robotic arms move in unison. Therefore controlled table movement is feasible without the need for undocking and redocking. (see this page for more info on ITM)
References

No Comments