Skip to main content
Obstetric Anesthesia Considerations
General Considerations
-
Two patients i.e. mother and fetus
-
Maternal physiologic changes:
-
Cardiac output increases by 50% by 2nd trimester w/ increased HR & SV
-
Blood volume increases by 45% --> dilutional anemia
-
Hypercoagulable state --> increases risks of periop thromboembolic events
-
Aorto-caval compression w/ supine position --> oblique position for left uterine displacement --> prevents decrease in uterine blood flow and maternal hypotension
-
O2 consumption increases by 60%
-
Minute ventilation increases by 45% by increasing TV
-
FRC decreases by 20% (30% in supine) --> decreased safe duration of apnea
-
Delayed gastric emptying & increased intraabdominal pressure --> GERD --> aspiration prophylaxis e.g. 30ml NaCitrate, 10mg metoclopramide IV, 50mg ranitidine IV; RSI w/ cricoid pressure in case of GA
-
Reduced MAC by 30%
-
Reduced LA requirement by 25%
-
Renal blood flow increased by 75% --> GFR increased by 50%
-
Sizeable breasts, airway edema --> potential difficult airway
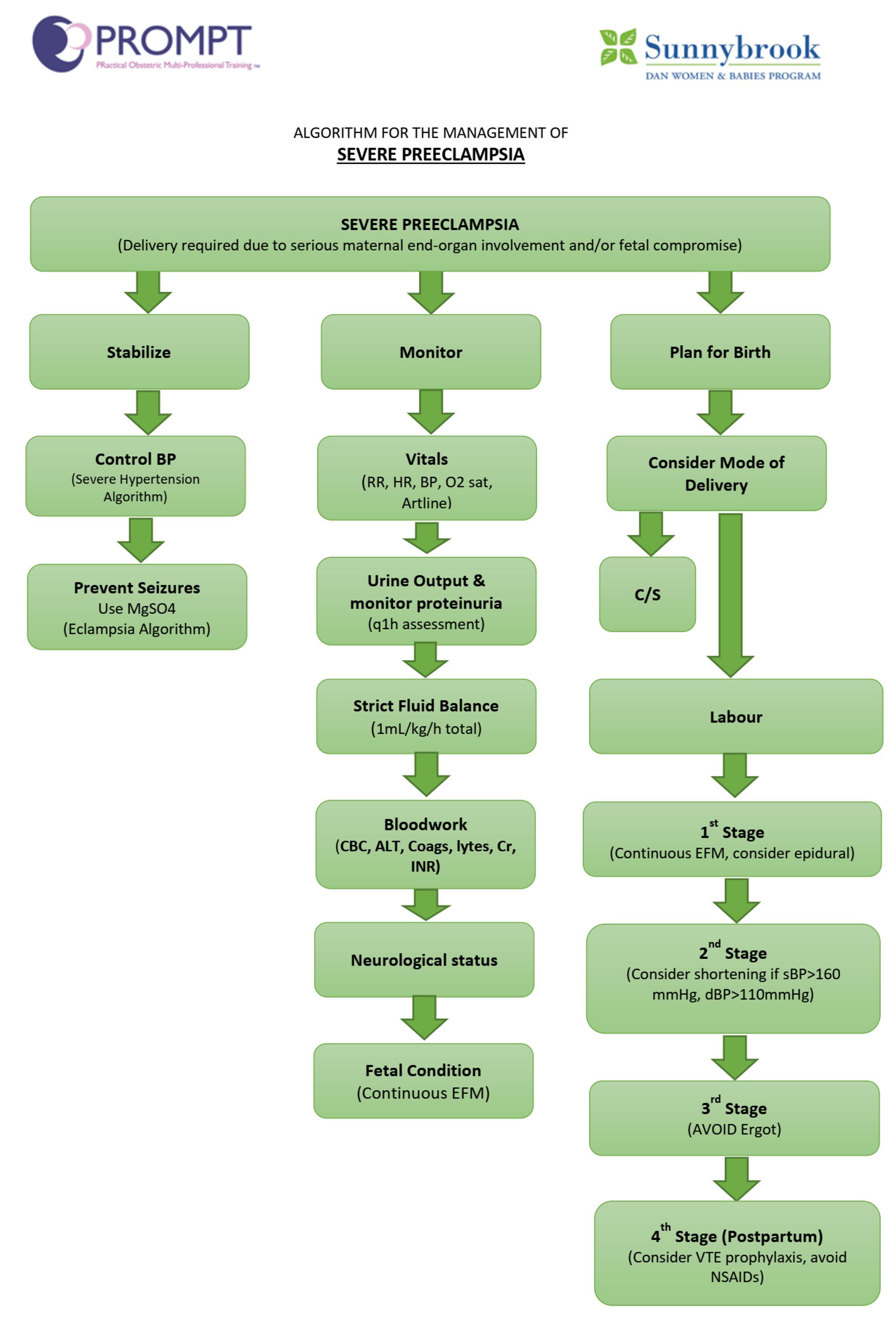
Preeclampsia
-
Semi-urgent to urgent
-
Risk factors:
-
Family hx of PIH
-
Chronic HTN?
-
Previous hx of preeclampsia?
-
Co-existing vascular / endothelial disease (e.g. chronic renal diseases, lupus, protein S deficiency etc.)
-
Nulliparity, > 40yo, multiple gestations, DM, obesity?
-
Multisystem involvement:
-
Airway w/ internal and external edema --> potential difficult airway
-
Pulmonary edema - uncommon; reduced colloid oncotic pressure, endothelial dysfunction and diastolic dysfunction predisposed to development of pulmonary edema
-
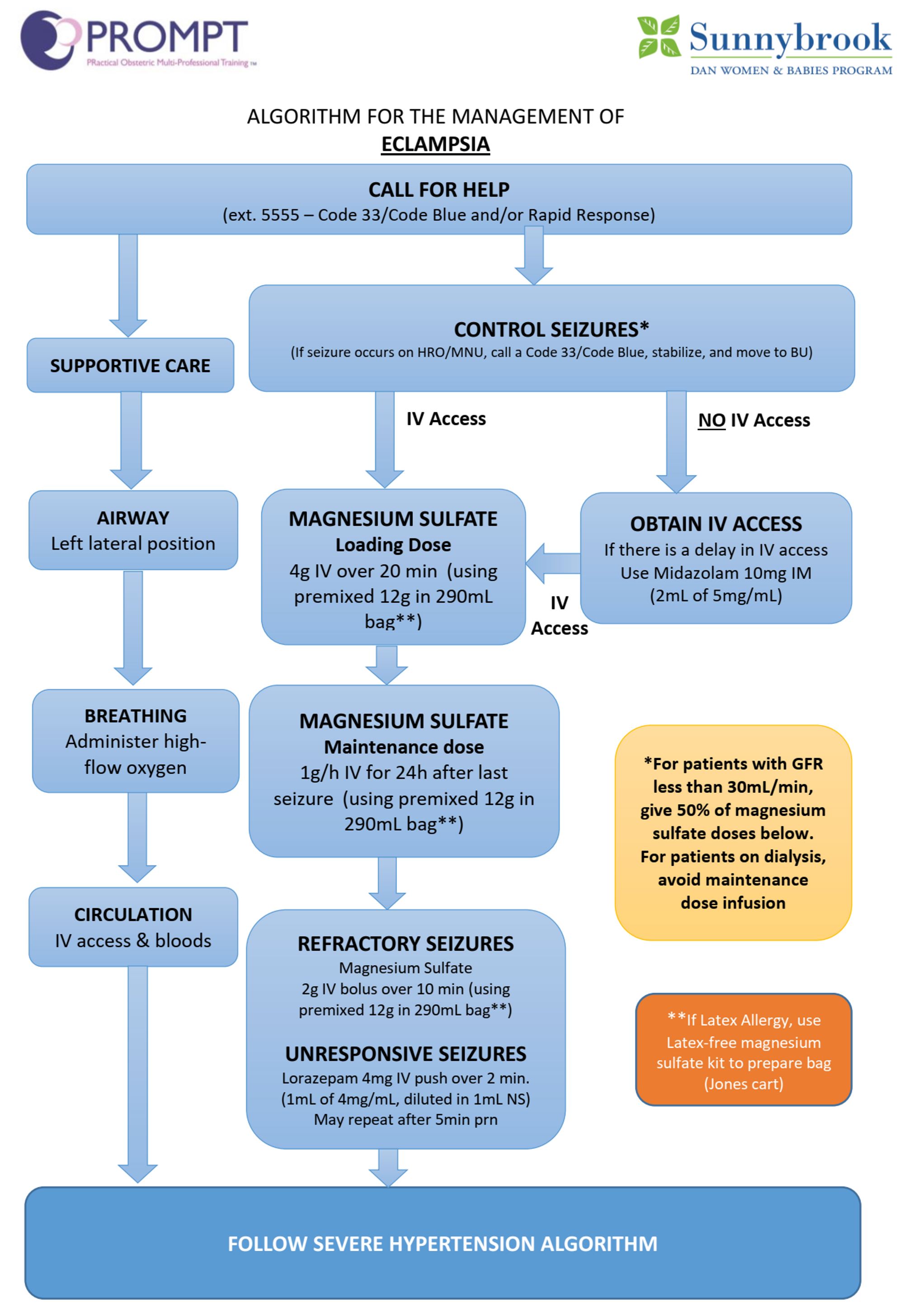
CNS involvements e.g. cerebral edema, ICH, increased ICP, HA, visual disturbance, altered mentation, seizure
-
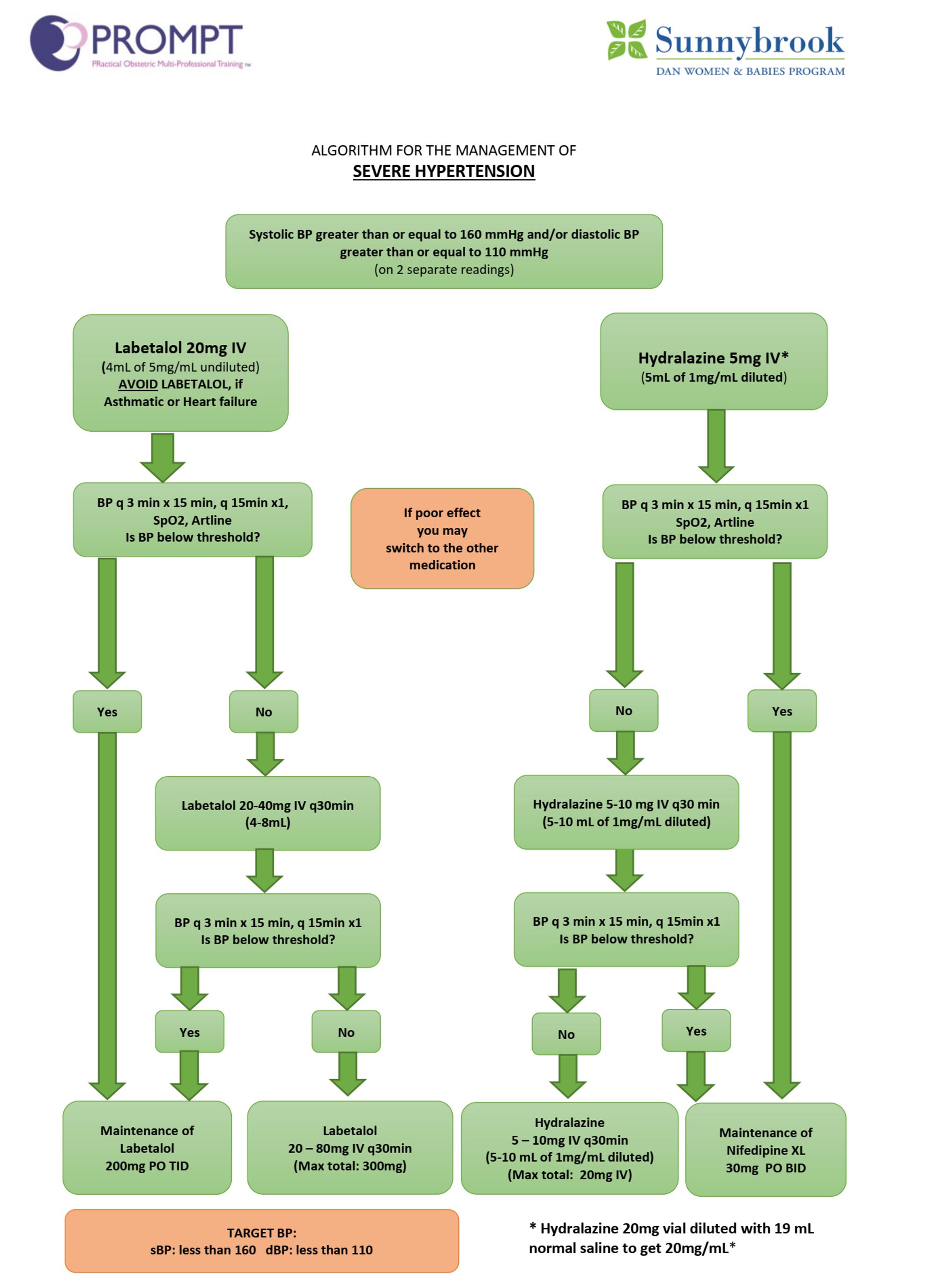
Hypertension, labile BP --> Art line prior to GA induction; NTG, phenylephrine readily available during induction; hypertensive crisis, LV dysfunction / cardiomyopathy / CHF
-
Reduced intravascular volume --> cautious with neuraxial blockade; volume expansion prior to spinal/epidural; phenylephrine readily available
-
Coagulopathy --> early insertion of epidural catheter before any coagulopathy, epidural is also partially therapeutic
-
Hemolysis, Elevated Liver enzymes, Low Platelets
Platelets < 50 neuraxial technique contraindicated
50-70: risk vs benefit judgement (consider trend, other competing factors e.g. airway, cardiac / neuro status)
>70: likely safe
-
Renal impairment due to glomerular endotheliosis
-
Uteroplacental unit; increased chance of abruptio placenta
-
Risks to baby: IUGR, increased risk of fetal asphyxia, IUD, prematurity
-
Goals:
-
BP control (sBP <160 mmHg, dBP <110 mmHg)
-
Optimize volume status
-
Maintain adequate uteroplacental perfusion
-
Minimize end-organ issues e.g. seizures, ICH, cardiac ischemia
-
Optimize labour analgesia to minimize exacerbation of BP due to pain
-
Pharmacological intervention:
-
MgSO4 4g IV over 10-15min, then 1-3g per hour for maintenance; constant monitoring of cardiopulmonary status, knees DTR, urine output; Ca gluconate 1g IV over 3-5min in case of overdose
-
MgSO4 also for neuroprotection in premature babies
-
Hyralazine 5-10mg IV bolus, then 5mg per hour
-
Labetolol 20mg IV repeated q15min prn, 20mg/hr maintenance