Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre Perioperative Protocol for Patients on GLP-1 Receptor Agonists
By Dr. J Huang & Dr. M Gulak - October 2023
Background:
- Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs or GLP-1 agonists) such as Ozempic (semaglutide) are prescribed for type 2 diabetes and more recently weight loss, with a large surge in prescribing in the last year
- GLP-1 agonists delay gastric emptying and can have very long half-lives (i.e., 7 days for semaglutide)
- There is increasing concern for patients presenting for elective procedures with full stomachs and experiencing regurgitation/pulmonary aspiration despite appropriately fasting (up to 20h)1-3
Scope:
- Elective and planned surgeries and procedures requiring anesthesia
Aim:
- To minimize the risk of regurgitation/pulmonary aspiration under anesthesia in patients taking GLP-1 agonists while accounting for the practical challenges of a prolonged medication hold
Preoperative Recommendations:
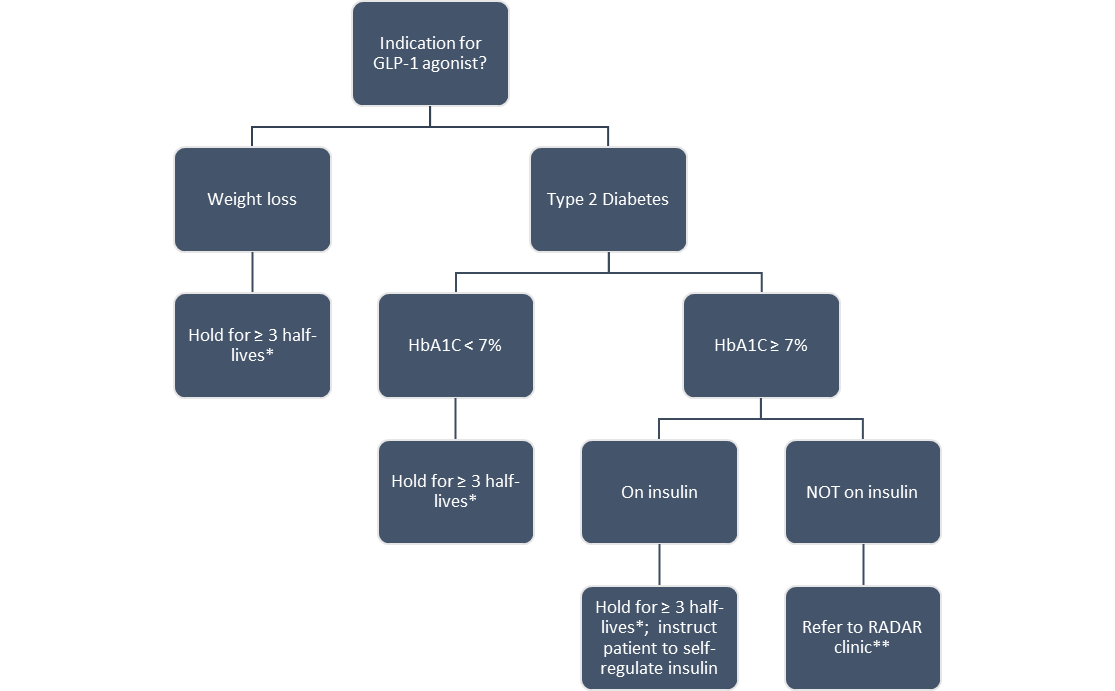
1. Patients taking GLP-1 agonists for weight loss
Recommendation: Hold GLP-1 agonist for ≥3 half-lives prior to surgery, i.e., 3 weeks for Ozempic (semaglutide)
2. Patients taking GLP-1 agonists for type 2 diabetes
Consider:
- How recently has the GLP-1 agonist been started?
- What is the risk of hyperglycemia if the GLP-1 agonist is held?
- Does the patient take insulin and can they self-regulate their glycemic control if the GLP-1 agonist is held?
Recommendations (to be adjusted based on above considerations):
- If Hb1AC <7%: Hold GLP-1 agonist for ≥3 half-lives prior to surgery, i.e., 3 weeks for Ozempic (semaglutide)
- If HbA1C ≥7% and taking insulin:
~ Hold GLP-1 agonist for ≥3 half-lives AND instruct patient to self-regulate glycemic control
- If HbA1C ≥7% and NOT taking insulin:
~ Refer to RADAR clinic (rapid referral endocrinology clinic) preoperatively
- If no HbA1C available, draw one in PAC, refer to RADAR if necessary. If not enough time before surgery, treat as per perioperative diabetic protocol. Hold GLP-1 agonist.
Day of Procedure Recommendations:
3. GLP-1 agonist appropriately held
Recommendation: Proceed as usual
4. GLP-1 agonist NOT appropriately held
Recommendation: Anesthesiologist should use clinical judgement regarding proceeding vs. delaying
- Consider treating patient as a full stomach if proceeding
- Consider delaying if any GI symptoms (nausea, vomiting, bloating, abdominal pain)
- Consider use of gastric ultrasound to determine stomach contents
Additional Considerations:
- Currently, no evidence to guide modification of fasting duration/regimens for these patients
- Avoid increasing the dose of GLP-1 agonist prior to elective surgery as this tends to precipitate side effects
- Although Ozempic (semaglutide) is most likely to be encountered, other GLP-1 agonists have varying half-lives which should be accounted for (see algorithm below)
Proposed Algorithm for Patients Presenting to Preassessment Clinic on GLP-1 agonists:
* The recommendation for 3 half-lives is adapted from Jones et al. (CJA 2023)4 and is based on balancing pharmacokinetic principles (87.5% drug elimination) with the practicality of a prolonged medication hold. It should be determined based on the following:
- Semaglutide (Ozempic, Wegovy) – weekly injection, half-life = 7 days
- Semaglutide (Rybelsus) – daily oral tablet, half-life = 7 days
- Tirzepatide (Mounjaro) – weekly injection, half-life = 5 days
- Dulaglutide (Trulicity) – weekly injection, half-life = 4.5 days
- Liraglutide (Victoza, Saxenda) – daily injection, half-life = 12.5 hours
- Lixisenatide (Adylxin) – daily injection, half-life = 3 hours
** RADAR clinic is the rapid referral endocrinology clinic at Sunnybrook
References:
1. Klein SR, Hobai IA. Semaglutide, delayed gastric emptying, and intraoperative pulmonary aspiration: a case report. Can J Anaesth. 2023 Aug;70(8):1394-1396. English. doi: 10.1007/s12630-023-02440-3. Epub 2023 Mar 28.
2. Gulak MA, Murphy P. Regurgitation under anesthesia in a fasted patient prescribed semaglutide for weight loss: a case report. Can J Anaesth. 2023 Aug;70(8):1397-1400. English. doi: 10.1007/s12630-023-02521-3. Epub 2023 Jun 6.
3. Beam WB, Hunter Guevara LR. Are serious anesthesia risks of semaglutide and other GLP-1 agonists under-recognized? Case reports of retained solid gastric contents in patients undergoing anesthesia. ASPF. 2023 Jun.
4. Jones PM, Hobai IA, Murphy PM. Anesthesia and glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists: proceed with caution! Can J Anaesth. 2023 Aug;70(8):1281-1286. English. doi: 10.1007/s12630-023-02550-y. Epub 2023 Jul 19.
Addendum
Summary of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists for Adults*
|
Generic Drug |
Brand Name |
Indications/ |
Gastric Emptying/ |
Mechanism of Action* |
Add-on Therapy |
Adverse Effects |
|
Dulaglutide |
Trulicity |
T2D |
Delayed by ~120 min, where the effect is largest after the first dose and diminishes with subsequent doses. |
↑ intracellular cyclic AMP in pancreatic β cells leading to glucose-dependent insulin release. ↓ glucagon secretion and slows gastric emptying |
Optional as monotherapy, or as add-on to OADs +/ insulin |
Mild to moderate: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea Hypoglycemia Acute pancreatitis (rare) |
|
Exenatide (ER) |
Bydureon BCise |
T2D |
2.4 h/Sustained release (t1/2) |
Binding of the drug to pancreatic GLP-1 receptors mediates: ↑ glucose-dependent insulin secretion from pancreatic β cells Suppresses glucagon secretion and delays gastric emptying Reduces food intake |
None |
Nausea (less occurrence compared to twice daily dose) Injection-site nodule |
|
Exenatide (IR) |
Byetta |
T2D/Obesity |
100-120 min |
Same as ER version |
None |
nausea irritation at injection site |
|
Liraglutide |
Saxenda |
Obesity |
70 min (median) |
Delays gastric emptying of solids Effects to relevant phenotype and genotypic biomarkers of gastrointestinal functions (variants GLP1R and TCFL2 genes) |
None |
nausea diarrhea abdominal pain/discomfort constipation |
|
Liraglutide |
Victoza |
T2D |
13 h (t1/2) |
Induced weight loss ↑ glucose-dependent insulin release Improved insulin secretion/β-cell function Reduced liver fat content |
+/- long-acting insulin |
hypoglycemia GI-tract events increased pulse rate |
|
Lixisenatide |
Adlyxin |
T2D |
3 h (t1/2) |
Weight loss Delays gastric emptying Delays intestinal glucose absorption Reduces postprandial insulin secretion May indirectly suppress glucagon secretion |
+/- long-acting insulin |
hypoglycemia nausea (moderate) vomiting injection site reaction headache dizziness |
|
Semaglutide |
Ozempic, Wegovy, others |
T2D/Obesity |
60 minutes |
↓ glucagon secretion Delays gastric emptying |
+/- long-acting insulin |
nausea diarrhea constipation |
|
Semaglutide |
Rybelsus |
T2D |
60 minutes |
Delays gastric emptying ↓ in HbA1c Weight loss ↓ systolic blood pressure |
+/- long-acting insulin |
nausea diarrhea |